Just In Time Compiler - Part 2. Brainfuck compiler and Interpreter
# Part 2. Brainfuck compiler and Interpreter
用最簡單的圖靈完全語言 Brainfuck 程式,寫一個 Brainfuck 的 compiler 及 interpreter
# 一、Brainfuck 簡介
Brainfuck 是一個圖靈完全語言,你可以用它做一個作業系統,也可以做和其他程式語言一樣的事情
只需要無限長的紙帶 (tape)、計數器、當前指標位置及來源程式碼就好
Brain fuck與 C 語言 對照表
Brainfuck C 含義 > ++ptr; 指標加一 < --ptr; 指標減一 + ++*ptr; 指標指向的位元組其值加一 - --*ptr; 指標指向的位元組其值減一 . putchar(*ptr); 輸出指標指向的位元組內容 (ASCII 碼) , *ptr=getchar(); 輸入內容到指標指向的位元組 (ASCII 碼) [ while(*ptr){ 如果指標指向的位元組其值為零,向後跳轉到對應的 ] 指令的次一指令處 ] } 如果指標指向的位元組其值不為零,向前跳轉到對應的 ] 指令的次一指令處 所以下列兩者是等價的
+++++ [ - ]1
2
3
41
2
3
4*p += 5; while(0 != *p) { *p--; }1
2
3
41
2
3
4另外推薦一個網站,Brainfuck Interpterer and Tape Visualizer (opens new window) 可以很清楚的看到 BF 怎麼運作
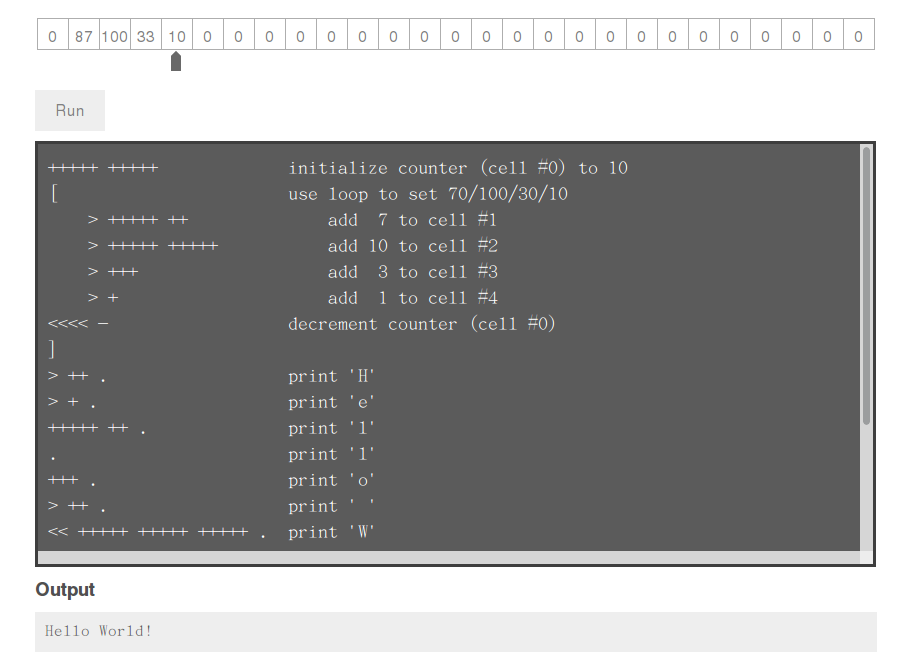
那先試試看執行 Brainfuck 吧,先安裝 brainfuck 編譯器
sudo apt install bf
之後建立 hello.bf
++++++++++[>+++++++>++++++++++>+++>+<<<<-]
>++.>+.+++++++..+++.>++.<<+++++++++++++++.
>.+++.------.--------.>+.>.
2
3
2
3
執行以下指令,即可得到 Hello world!
bf hello.bf
# 二、Brainfuck 編譯器及直譯器
# 2.1 利用 sed 打造簡單的編譯器
誠如 Jserv (opens new window) 所言,打造一個 Brainfuck 編譯器是很簡單的,廣義的編譯器就是將一種語言轉成另外一種語言,例如
- SaSS 之於 CSS
- Typescript 之於 Javascript
- C 之於 組合語言
等等,我們也可以將 C 語言視為 Brainfuck 的低階語言,並利用上面的對照表,直接用 sed 就可以實現了,以下程式也是 Jserv's blog (opens new window) 提供的
#! /bin/sed -f
s/[^][+<>.,-]//g
s/\([-+]\)/\1\1*p;/g
s/</p--;/g
s/>/p++;/g
s/\./putchar(*p);/g
s/,/*p=getchar();/g
s/\[/while (*p) {/g
s/\]/}/g
1s/^/#include <stdlib.h>\n#include <stdio.h> \nint main(void){char *p=calloc(1,10000);/
$s/$/}/
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
解釋:
s/[^][+<>.,-]//g: 把不是[^][+<>.,-]的字元變成空字串的s/\([-+]\)/\1\1*p;/g: 匹配到 - 或是 + 變成--*por++*p1s/^/#include <stdlib.h>\n#include <stdio.h> \nint main(void){char *p=calloc(1,10000);/在一開始^的地方插入#include <stdlib.h>...1s 為第一行$s/$/}/: 在最後一行結尾加入}
輸入指令
sed -f BF_2_C.sed hello.bf
輸出
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void){char *p=calloc(1,10000);++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;while (*p) {p++;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;p++;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;p++;++*p;++*p;++*p;p++;++*p;p--;p--;p--;p--;--*p;}
p++;++*p;++*p;putchar(*p);p++;++*p;putchar(*p);++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;putchar(*p);putchar(*p);++*p;++*p;++*p;putchar(*p);p++;++*p;++*p;putchar(*p);p--;p--;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;++*p;putchar(*p);
p++;putchar(*p);++*p;++*p;++*p;putchar(*p);--*p;--*p;--*p;--*p;--*p;--*p;putchar(*p);--*p;--*p;--*p;--*p;--*p;--*p;--*p;--*p;putchar(*p);p++;++*p;putchar(*p);p++;putchar(*p);}
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
# 2.2 打造BF的直譯器
由上面的映射表,BF 直譯器可以簡單用 C 語言不到 100 行表示,
// input is a const array to const char.
void interpreter(const char input[])
{
// ASCII 8 bit.
uint8_t tape[30000] = { 0 };
// set pointer to the left most cell of the tape.
uint8_t *ptr = tape;
char current_char;
for(int i = 0 ; (current_char = input[i]) != '\0'; i++)
{
switch(current_char)
{
case '>':
++ptr;
break;
case '<':
--ptr;
break;
case '+':
++(*ptr);
break;
case '-':
--(*ptr);
break;
case '.':
putchar(*ptr);
break;
case ',':
*ptr = getchar();
break;
case '[':
if (!(*ptr)) // counter = 0, go to the end bracket
{
int loop = 1;
while (loop > 0)
{
current_char = input[++i];
if (current_char == ']')
{
--loop;
}
else if (current_char == '[')
{
++loop;
}
}
}
break;
case ']':
if (*ptr)
{
int loop = 1;
while (loop > 0) // back to start bracket
{
current_char = input[--i];
if (current_char == '[')
{
--loop;
}
else if (current_char == ']')
{
++loop;
}
}
}
break;
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 2)
{
err("Usage: interpreter <inputfile>");
}
char *file_contents = read_file(argv[1]);
if (file_contents == NULL)
{
err("Couldn't open file");
}
interpreter(file_contents);
free(file_contents);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
其中比較需要思考的是[]的部分,利用tape上紀錄count,以下是虛擬碼
if 遇到 ] 且 count != 0 : 回去最初的 [
if 遇到 [ 且 count == 0 : 直接跳至最後的 ]
2
2
編譯並執行就可以變成BF的直譯器囉❤
# 2.3 打造BF的編譯器
這裡稍微複雜一點,因為我們要根據不同的指令集架構,把 BF 轉成平台對應的組合語言,這裡就不向上面直譯器一樣有可移植性,因為要產生平台相依的程式碼。這裡直接用Jserv's Github (opens new window),我的組合語言能力不太好 ༼ つ ◕_◕ ༽つ,以下是x64架構的組合語言,仔細講解的地方可以參考interpreter-compiler-jit (opens new window)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "util.h"
void compile(const char * const text_body)
{
int num_brackets = 0;
int matching_bracket = 0;
struct stack stack = { .size = 0, .items = { 0 } };
const char * const prologue =
".text\n"
".global main\n"
"main:\n"
" pushq %rbp\n"
" movq %rsp, %rbp\n"
" pushq %r12\n" // store callee saved register
" subq $30008, %rsp\n" // allocate 30,008 B on stack, and realign
" leaq (%rsp), %rdi\n" // address of beginning of tape
" movl $0, %esi\n" // fill with 0's
" movq $30000, %rdx\n" // length 30,000 B
" call memset\n" // memset
" movq %rsp, %r12";
puts(prologue);
for (unsigned long i = 0; text_body[i] != '\0'; ++i) {
switch (text_body[i]) {
case '>':
puts(" inc %r12");
break;
case '<':
puts(" dec %r12");
break;
case '+':
puts(" incb (%r12)");
break;
case '-':
puts(" decb (%r12)");
break;
case '.':
// move byte to double word and zero upper bits
// since putchar takes an int.
puts(" movzbl (%r12), %edi");
puts(" call putchar");
break;
case ',':
puts(" call getchar");
puts(" movb %al, (%r12)");
break;
case '[':
if (stack_push(&stack, num_brackets) == 0) {
puts (" cmpb $0, (%r12)");
printf(" je bracket_%d_end\n", num_brackets);
printf("bracket_%d_start:\n", num_brackets++);
} else {
err("out of stack space, too much nesting");
}
break;
case ']':
if (stack_pop(&stack, &matching_bracket) == 0) {
puts(" cmpb $0, (%r12)");
printf(" jne bracket_%d_start\n", matching_bracket);
printf("bracket_%d_end:\n", matching_bracket);
} else {
err("stack underflow, unmatched brackets");
}
break;
}
}
const char *const epilogue =
" addq $30008, %rsp\n" // clean up tape from stack.
" popq %r12\n" // restore callee saved register
" popq %rbp\n"
" ret\n";
puts(epilogue);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 2) err("Usage: compiler-x64 <inputfile>");
char *text_body = read_file(argv[1]);
if (text_body == NULL) err("Unable to read file");
compile(text_body);
free(text_body);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
利用輸出的組合語言,再重導向到 ***.S檔案,就可以利用 gcc 進行編譯了,參照以下的 makefile
BF_COMPILER_X64 = BF_compiler_x64
all: $(BF_COMPILER_X64)
$(BF_COMPILER_X64): $(BF_COMPILER_X64).c
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -o $@ $^
run_compiler: $(BF_COMPILER_X64)
./$< hello.bf > hello.s
$(CC) -o hello-x64 hello.s
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
可以看到先把 BF compiler 編譯完成,再用編譯好的 BF compiler 把 BF code 編譯成 x64 的組合語言,最後再編譯該組合語言成執行檔。
這邊需要深入了解組合語言
# 專案執行
- 建立
sed把 BF 轉成 C code 再編譯
make sed_BF; ./sed_BF
- 建立 BF 的直譯器
make BF_interpreter; ./BF_interpreter hello.bf
- 建立 BF 的編譯器
make BF_compiler_x64; make run_compiler; ./hello-x64
